Could a light-harvesting protein phycocyanin be used as a novel drug against Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [1, 2]?
In the present study, intact hexameric phycocyanin was isolated and crystallized from the cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. N62DM, and the structure was solved to a resolution of 2.6 Å. Molecular docking studies show that the phycocyanin αβ-dimer interacts with the enzyme β-secretase, which catalyzes the proteolysis of the amyloid precursor protein to form plaques. The molecular docking studies suggest that the interaction between phycocyanin and β-secretase is energetically more favorable than previously reported inhibitor-β-secretase interactions. Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans worms, with a genotype to serve as an AD-model, were significantly protected by phycocyanin. Therefore, the present study provides a novel structure-based molecular mechanism of phycocyanin-mediated therapy against AD.
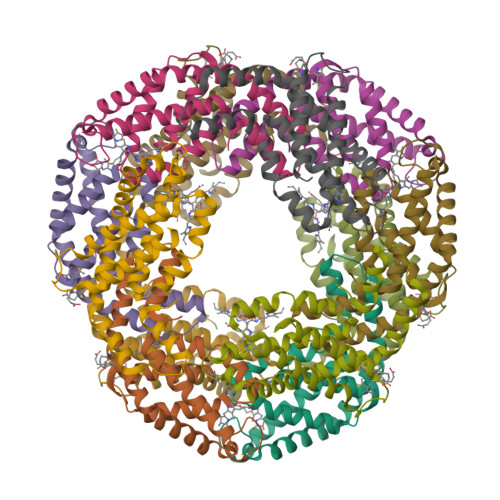
- Singh, N.K., Hasan, S.S., Kumar, J., Raj, I., Pathan, A.A., Parmar, A., Shakil, S., Gourinath, S. and Madamwar D. (2014) Crystal structure and interaction of phycocyanin with β-secretase: A putative therapy for Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 13, 691—698.
- PDB:4L1E




